UPDATE: A groundbreaking study from a collaborative team at Jiangsu University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hasselt University, and MIT reveals a revolutionary approach to electrolysis that could transform sustainable energy production. Published online in eScience in July 2025, this comprehensive review addresses the urgent need for cleaner, more efficient energy and chemical processes.
For over two centuries, fossil fuels have dominated global energy production, contributing to over 80% of consumption and leading to severe environmental degradation. The new findings underscore the critical transition towards renewable energy sources, which remain hampered by inefficiencies in traditional chemical processes. The research team highlights the promise of electrochemistry powered by renewables, emphasizing the need to replace the inefficient oxygen evolution reaction (OER) with more effective reactions.
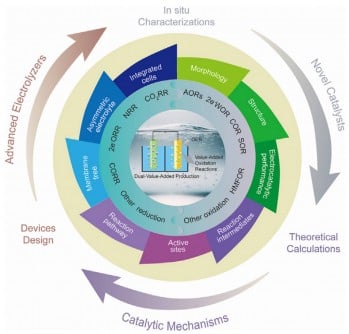
The study outlines a roadmap for integrated electrosynthesis systems that can produce valuable by-products while generating clean fuels. By coupling alternative oxidation reactions—such as methanol and glycerol oxidation—with reduction processes like CO2 reduction (CO2RR) and nitrogen reduction (NRR), the authors demonstrate a path to achieve dual outputs with significantly reduced energy consumption.
Prof. Zhenhai Wen, along with colleagues Prof. Hao Zhang and Prof. Nianjun Yang, state,
“Electrochemical systems that simultaneously produce two valuable outputs represent a paradigm shift for green chemistry.”
Their research indicates that replacing OER with alternative oxidation reactions can dramatically enhance system efficiency, yielding valuable chemicals such as formic acid and hydrogen peroxide.
Innovations in catalyst development, particularly with nanostructured materials, are central to this progress. These advancements expand active sites and improve selectivity, which is crucial for scaling these processes. The use of hybrid electrolyzers and advanced spectroscopic techniques also facilitates real-time monitoring of catalytic processes, paving the way for industrial-scale implementation.
The implications of these findings are profound, potentially reshaping the energy and chemical sectors. The researchers assert that dual-value electrosynthesis systems not only help in reducing carbon emissions but also enable the economical production of green hydrogen, fuels, and fertilizers. By integrating advanced catalysts and computational methods into the design of these systems, we can work towards a more sustainable and circular chemical industry.
As the world grapples with climate change and resource challenges, the dual-benefit approach of this research offers a promising avenue for energy, environmental, and industrial advancements. The development of these systems could significantly contribute to global net-zero goals while creating new opportunities for renewable-driven industrial chemistry.
For more details, view the study at DOI: 10.1016/j.esci.2024.100333.
This urgent research is a call to action for policymakers, industry leaders, and researchers to accelerate the transition to sustainable practices that can mitigate climate impacts and foster economic growth. Share this crucial development within your networks and stay informed on the future of sustainable energy innovation.