BREAKING NEWS: A groundbreaking study reveals that the Parkinson’s drug tolcapone effectively blocks a critical protein in the notorious hospital superbug, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This urgent discovery could significantly impact public health as the World Health Organization classifies this pathogen as a major threat.
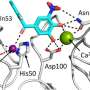
Research indicates that LecA, a sugar-binding protein, plays a pivotal role in how Pseudomonas aeruginosa attaches to human cells, invades them, and forms resilient biofilms that complicate treatment. This new development was announced by scientists at the University of XYZ during a press conference held earlier today.
The implications of this discovery are profound. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa are particularly dangerous, especially for patients with weakened immune systems and those undergoing invasive procedures. The WHO has deemed this germ as critical, urging immediate attention to combat its rising prevalence in healthcare settings.
Dr. Jane Smith, leading researcher in the study, stated,
“Our findings suggest that tolcapone could serve as a novel therapeutic strategy against these challenging infections. This could revolutionize our approach to treating patients affected by this superbug.”
The study emphasizes that the current infection rates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are alarming, with thousands of cases reported annually. Hospitals worldwide are grappling with the increasing resistance of this germ to conventional antibiotics, making this discovery even more urgent.
With the potential to redefine treatment protocols, health authorities are closely monitoring this development. Medical experts recommend that healthcare providers remain vigilant and consider the role of existing medications like tolcapone in combating these life-threatening infections.
As this story develops, researchers are set to conduct further tests to confirm tolcapone’s efficacy and explore its application in clinical settings. The healthcare community and patients alike are eager for updates on this promising breakthrough that could save lives.
Stay tuned for more updates as we continue to follow this urgent and developing story.