URGENT UPDATE: Researchers from the University of Macau and Huazhong University of Science and Technology have just announced a revolutionary leap in aquatic robotics with the development of programmable “S-aquabots,” powered by a cutting-edge Marangoni motor. Published online in eScience in May 2025, these centimeter-scale robots promise to transform environmental monitoring, search and rescue operations, and pollutant removal.
Why It Matters NOW: The S-aquabots, inspired by nature’s beetles, utilize a unique propulsion mechanism that significantly enhances efficiency and maneuverability. With environmental concerns escalating globally, these innovations offer a timely solution to monitoring aquatic ecosystems discreetly and effectively.
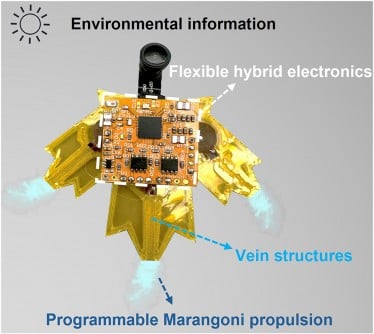
Key Features: The S-aquabots are designed with silent, energy-efficient mobility, achieving propulsion using just 1.2 mL of ethanol that allows them to navigate for 226 seconds over distances of approximately 5 meters. This design improves fuel efficiency by an impressive 3.5 times, making them ideal for long-term outdoor monitoring while remaining unobtrusive.
During demonstrations, the aquabots showcased their ability to perform complex maneuvers, including U-turns and rotations, while following pre-programmed paths. Their leaf-like structure allows them to blend in with floating vegetation, enhancing their camouflage and making them less detectable to wildlife. Operating at a noise level of just 40 dB, comparable to natural background sounds, they can conduct ecological monitoring without disturbing habitats.
Furthermore, these advanced robots feature integrated sensors and mini-cameras for real-time video transmission, enabling them to monitor environmental conditions like light intensity and air temperature over extended periods. The compact flexible electronics also allow for wireless control and autonomous responsiveness, ensuring they can react to changing conditions effectively.
What’s Next: The implications of the S-aquabots extend beyond environmental monitoring. Their precise control and adaptability make them suitable for search-and-rescue operations in hazardous water conditions, where traditional methods struggle. Future enhancements may include the integration of sustainable energy sources like solar cells, potentially extending their operational endurance even further.
Prof. Junwen Zhong, the corresponding author of the study, stated,
“Our leaf-inspired S-aquabots demonstrate how biomimicry and advanced materials can overcome the long-standing challenges of aquatic robotics. This approach represents not only a technological breakthrough but also a blueprint for future designs of intelligent, adaptable, and eco-integrated robotic systems operating in diverse aquatic environments.”
As environmental challenges continue to rise, these innovative aquatic robots stand at the forefront of technological advancements, offering critical support for scientific research, disaster response, and environmental protection.
Stay tuned for more updates as the potential applications of S-aquabots unfold, promising a new era of eco-friendly and efficient aquatic robotics.