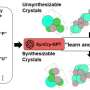
A research team at Seoul National University (SNU) has made significant strides in material science by developing an innovative technology that harnesses artificial intelligence (AI) to redesign materials that were previously challenging to synthesize. This breakthrough, led by Prof. Yousung Jung from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, utilizes large language models (LLMs) to create new forms of materials that are now experimentally feasible.
The team’s approach centers on the application of LLMs, which are typically used in natural language processing, to predict material properties and synthesis routes. By leveraging existing material databases, the AI can analyze complex interactions and suggest new combinations that scientists may not have considered. This method has the potential to accelerate the discovery of new materials significantly, which could have wide-ranging applications across various industries.
Transformative Potential in Material Science
The implications of this research extend beyond academic circles. Materials play a crucial role in sectors such as electronics, energy, and manufacturing. The ability to rapidly design and synthesize new materials could lead to innovations in battery technology, renewable energy sources, and even pharmaceuticals. For instance, materials that are more efficient in energy transfer could enhance the performance of solar panels or batteries, addressing critical issues in sustainability.
The research team tested their AI-driven methods on several known materials that have historically posed synthesis challenges. By applying the AI algorithms, they successfully identified new pathways for synthesizing these materials, demonstrating the technology’s effectiveness. This could pave the way for future research and development, allowing for the exploration of previously uncharted material properties.
A Collaborative Effort in Innovation
Prof. Jung emphasized the collaborative nature of this research, stating that the integration of AI into material science requires interdisciplinary efforts. The team collaborated with computer scientists and material scientists to refine the algorithms and ensure the accuracy of the predictions made by the AI. This amalgamation of expertise is crucial in developing a technology that is not only innovative but also practical for real-world applications.
As the research progresses, the team aims to publish their findings in reputable scientific journals, inviting further scrutiny and collaboration from the global scientific community. The ongoing work underscores a growing trend in which AI is becoming an indispensable tool in research and development across various fields.
In conclusion, the ability to redesign hard-to-synthesize materials using AI represents a significant advancement in material science. With the ongoing efforts led by Prof. Yousung Jung and his team at Seoul National University, the future of material synthesis is likely to be more efficient and innovative, potentially transforming industries and contributing to sustainable development goals.