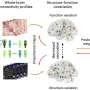
Recent advancements in machine learning are enhancing the ability to predict how patients will respond to antidepressants while effectively separating the drug effects from placebo responses. This innovation could significantly influence treatment approaches for the approximately 4% of the global population affected by depression, a prevalent mental health disorder characterized by persistent low mood, disrupted sleep and eating patterns, lack of motivation, and unhelpful thought processes.
Research teams are now harnessing machine learning algorithms to analyze data from extensive clinical trials, allowing healthcare professionals to tailor antidepressant prescriptions more accurately to individual patients. The integration of this technology aims not only to improve patient outcomes but also to minimize the trial-and-error approach often associated with antidepressant treatments.
Understanding the Impact of Machine Learning on Treatment
Depression’s widespread nature poses a significant challenge for healthcare providers. Traditional methods for determining the effectiveness of antidepressants can be cumbersome and subjective, often leading to delays in achieving optimal treatment. Researchers are exploring machine learning as a solution to enhance the accuracy of predictions regarding patient responses to medication.
By examining vast datasets, these algorithms can identify patterns that human clinicians may overlook. This predictive capability allows for a more nuanced understanding of how specific patients might react to various antidepressants, potentially reducing the time taken to find the right medication. The goal is to refine treatment plans based on individual characteristics, thereby increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Disentangling Drug Effects from Placebo Responses
A significant aspect of this research lies in the ability of machine learning to separate the effects of actual medication from those attributed to placebo. Understanding how much of a patient’s improvement is due to the drug itself versus psychological factors is crucial for developing effective treatment regimens.
The implications of these findings extend beyond merely enhancing treatment efficacy. They also hold the potential to reshape the approach towards clinical trials. As researchers gain insights into the placebo effect, they can design more robust studies that account for these variables, ultimately leading to better drug development processes.
In conclusion, the intersection of machine learning and mental health treatment represents a promising frontier in addressing depression. As researchers continue to refine these predictive models, the hope is that they will bring forth a new era in personalized medicine, providing patients with more effective solutions tailored to their unique needs.