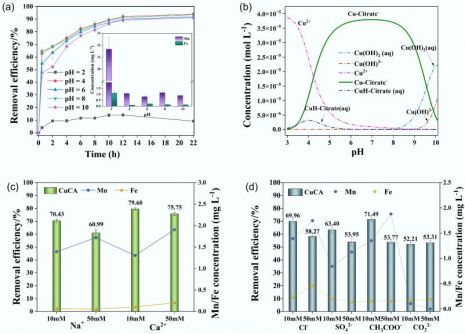
A team of researchers from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EEE) at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has made a significant advancement in artificial intelligence (AI) hardware. They have developed a new type of analog-to-digital converter (ADC) utilizing innovative memristor technology. This breakthrough, which is poised to enhance energy efficiency in AI systems, has been detailed in a recent publication in Nature Communications.
The newly designed ADC leverages the unique properties of memristors, which are passive two-terminal non-volatile memory components. By integrating these elements, the converter can operate with improved energy efficiency, which is critical for the growing demands of AI applications. The research team believes that this advancement could lead to substantial reductions in power consumption, a key factor in the sustainability of AI technologies.
Impact on AI Hardware Development
The development of this memristor-based converter comes at a time when the need for efficient AI hardware is more pressing than ever. Current AI systems often require vast amounts of energy, leading to increased operational costs and environmental concerns. The researchers assert that their ADC could serve as a foundational component for next-generation AI devices, enabling them to process data more efficiently while minimizing energy usage.
In addition to enhancing energy efficiency, the ADC’s design allows for faster data conversion rates. This capability is essential for high-performance AI applications, where speed and accuracy are paramount. According to the research team, the integration of memristor technology could facilitate the development of more sophisticated AI systems capable of handling complex tasks in real time.
Collaboration and Future Directions
This project is the result of a collaborative effort between various institutions, showcasing the importance of interdisciplinary research in advancing technology. The team includes experts in electrical engineering, materials science, and computer science, all working together to push the boundaries of what is possible in AI hardware.
Looking ahead, the researchers aim to further refine their memristor technology to enhance its scalability and applicability across different AI platforms. They are optimistic that ongoing research will lead to additional breakthroughs, potentially transforming the landscape of AI hardware in the coming years.
With the publication of their findings, the researchers hope to inspire further exploration and investment in memristor technology. As AI continues to evolve, innovations like this ADC will play a crucial role in ensuring that hardware keeps pace with the increasing demands of intelligent systems.
In summary, the development of this advanced memristor-based converter represents a pivotal step forward in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of AI hardware. As the research team at HKU continues their work, the implications of their findings may well extend far beyond the realm of artificial intelligence, influencing various fields that rely on high-performance computing.